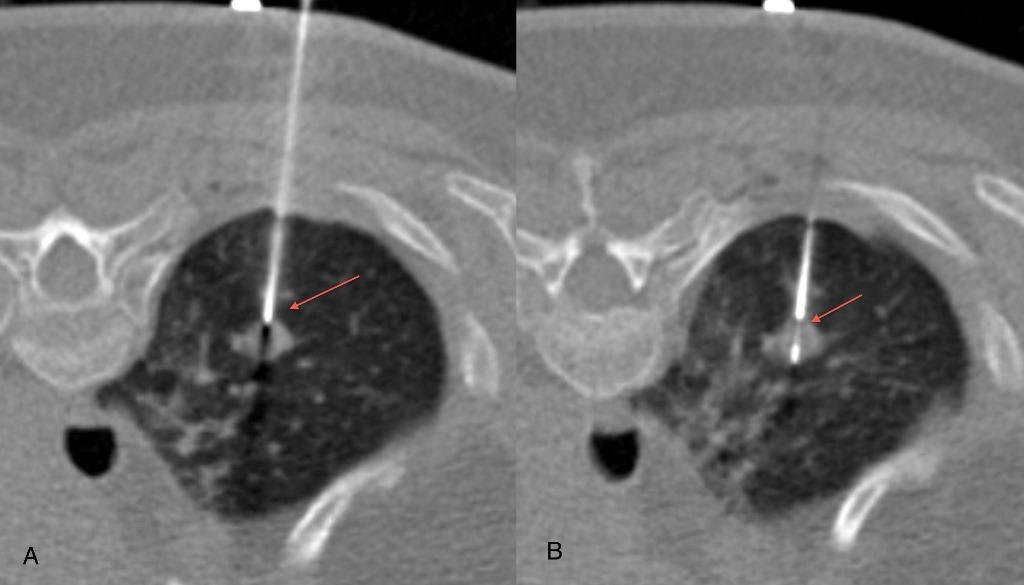
It is a medical procedure used by radiologist to take a sample from a suspected tumour or an organ. A CT scan is used for accurately localise the lesion and target it by biopsy needle with out any injury to adjacent vessel and other normal tissue.
If you taking blood-thinning medication e.g. Coumadin, or you are taking anti-diabetic medication, e.g Glucophage (Metformin)
If you are allergic to contrast, please call the above-mentioned numbers to report this condition.
You should have your last meal before midnight the day of the procedure. If you take blood pressure medication, please take it as scheduled with a sip of water.
MRI is an abbreviation used for Magnetic resonance imaging, which is a diagnostic service provided by the best of the hospitals. The test utilizes strong magnet and radio waves to develop a detailed and visually advanced image of the internal body organs and tissues. MRI is used to diagnose a number of medical conditions including cancer, heart, and vascular diseases, joint and musculoskeletal disorders, stroke, etc. It is a noninvasive diagnostic test which allows the doctor to view the organs in precise slices, one layer after another. It is one of the most detailed methods to explore all plains and angles with superior tissue image of any internal organ. By far, it is the most advanced imaging method for internal scans.
An MRI scan requires three basic components including a computer, magnetic field and radio waves. The three elements are used to create visually advanced and clear images of the internal organs of a human body. The human body has numerous hydrogen atoms, which are magnetic in nature. When the body is out into a magnetic field, these atoms align with the field’s intensity. With the radio wave, the MRI machine works against the polarity of these atoms and the time these atoms take to resume to their magnetic condition is measured using a sensor.
CAT/CT Scans
Computed Tomography, also known as CT or CAT Scan, it is a diagnostic procedure used to produce detailed X-ray images of the body to detect and reveal the details of internal organs and any health issues that cannot be seen by conventional X-rays. It can produce 2D cross-sectional images of the body’s tissues, bones, and blood vessels.
They use a narrow X-ray beam that circles around one part of your body. This provides a series of images from many different angles. A computer uses this information to create a cross-sectional picture. Like one piece in a loaf of bread, this two-dimensional (2D) scan shows a “slice” of the inside of your body.
This process is repeated to produce a number of slices. The computer stacks these scans one on top of the other to create a detailed image of your organs, bones, or blood vessels. For example, a surgeon may use this type of scan to look at all sides of a tumor to prepare for an operation.
Also known as an ultrasound, it is a kind of non-invasive imaging procedure that uses high-frequency waves to produce images of the internal organs. These images can provide valuable information about the tissues and organs such as the heart and abdomen to diagnose and treat a variety of diseases and conditions. Although most of these examinations involve placing the ultrasound equipment outside the body, a few may require using a device inside the body as wel
Purpose of Test
A sonogram image can show the sizes and shapes of structures, good and bad, inside the body. The harder and denser the tissue (bone would be the hardest and densest) the more it bounces sound waves back to the transducer and the brighter the resulting image becomes.
In an emergency setting, sonography will typically be performed right away. For a test on a future date, find out if you should, or should not, eat or drink anything before the test. For example, doctors will often ask you to fast (not eat or drink) for six hours before an abdominal ultrasound to look at the gallbladder, but tell you to drink several glasses of water and not urinate before a sonogram of the bladder.
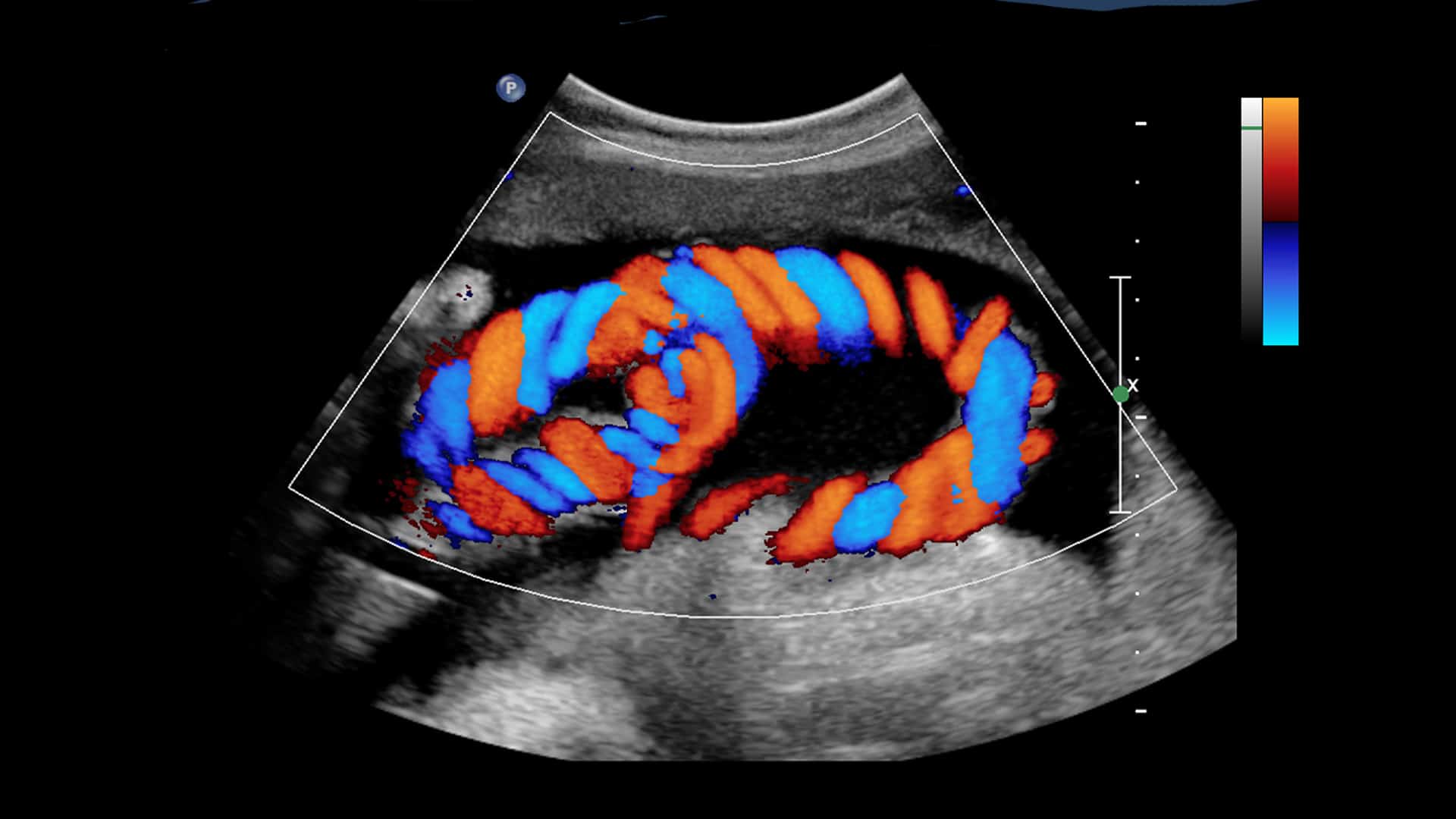
Colour Doppler Ultrasound Test
Colour Doppler is a type of ultrasound-based imaging technique used to visually observe blood flow through major arteries, blood vessels, and veins in the body and find any clots or blockages. In addition to this, for pregnant women, it is used to observe fetal heart and evaluate any birth deficiencies for the unborn baby. It uses high-frequency sound waves to generate the images.
Why Would I Need One?
Generally, it helps to wear loose-fitting clothes to the test, though your doctor may ask you to change into a gown. Also, you may want to leave jewelry at home, since you’ll have to remove it from any area to be tested.
Digital X-Ray Centre
An X-ray is a type of radiology service which involves a common imaging test that utilizes special equipment to create pictures of the parts inside the body that are denser. It uses low-dose electromagnetic radiation as compared to the traditional x-ray process and equipment. It can be used to examine various parts of the body such as bones, teeth, chest, and abdomen.
Digital radiography (digital X-ray) is a form of X-ray imaging where digital X-ray sensors are used instead of traditional photographic film. Advantages include increased efficiency by eliminating the need for chemical processing and the ability to digitally transfer and enhance images. Also, less radiation can be used to produce an image of similar contrast to conventional radiography.
What does a digital X-ray involve?
The digital X-ray procedure is highly similar to traditional X-rays; it is the technology that is very different. Bursts of radiation still pass through the body and form an image based on how much radiation passes through the different organs, but rather than using photographic film to capture the image, digital sensors are used.
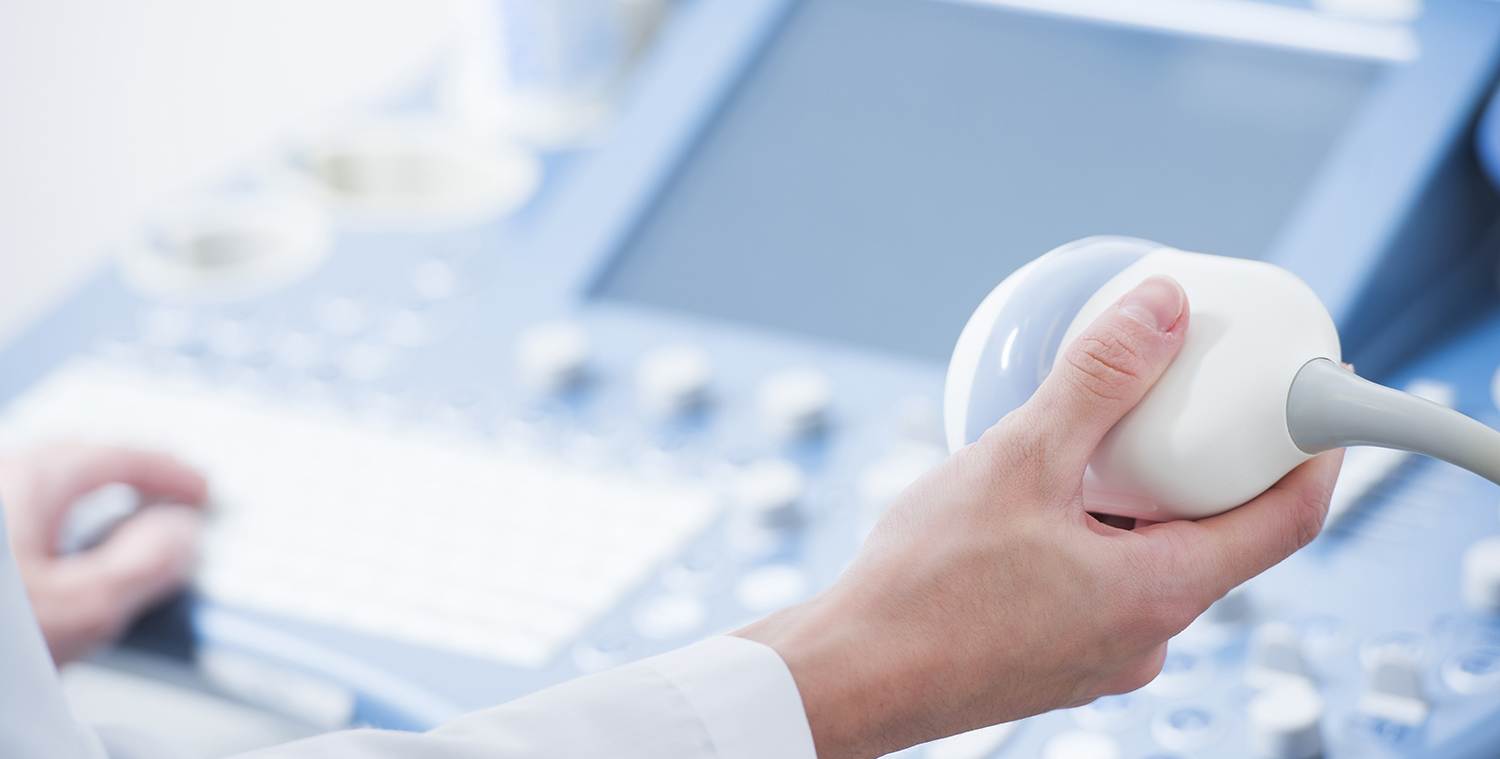

Also known as an ultrasound guided or sonography guided biopsy. It is an image-guided procedure that uses ultrasound to visualise the internal organs as well as mass or lesion and to take biopsy sample from appropriate site. It is often used for liver, breast, and lymph node biopsies and take the required tissue samples.
This test is most often used for lymph node, breast, and liver biopsies. This test can also be used with endoscopy or bronchoscopy when tumors are within the GI tract or the lungs. These are known as endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) or endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS).
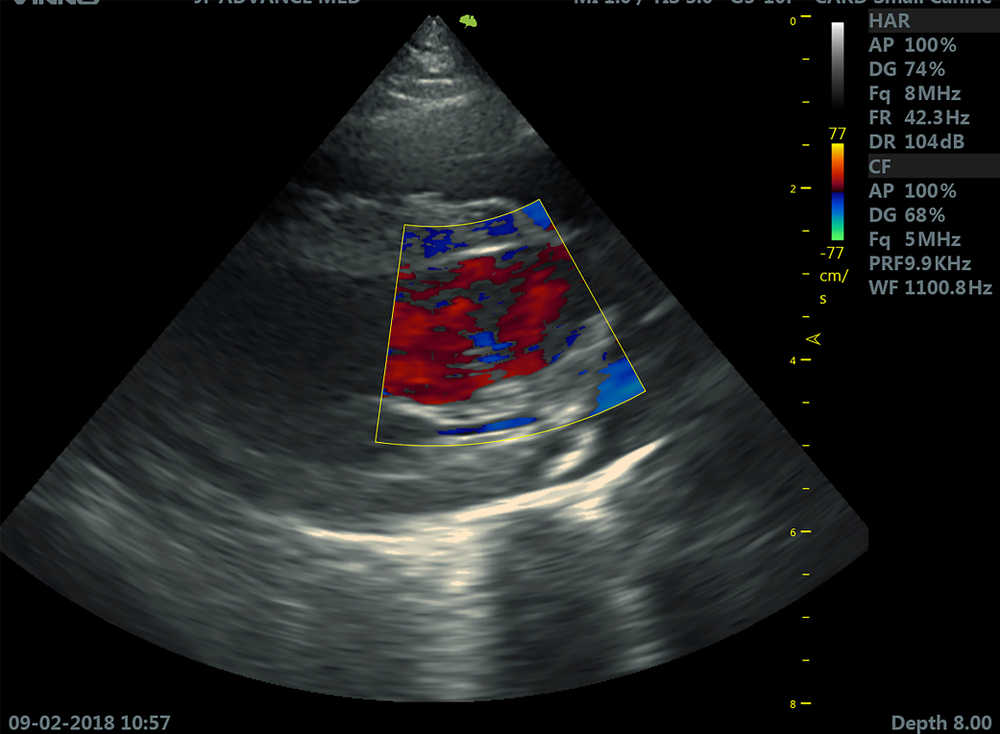
Also known as an echo cardiogram, it is used to study the heart’s movement using high-frequency or ultrasound waves. It also captures pictures of the valves and chambers in the heart and aids the sonographer in evaluating them. In addition to this, it helps to assess the functioning of the organ, follow its progress, and detects any disease.
The heart in your body pumps blood and the vascular system takes it to all the organs. Together they form the cardiovascular system. A healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced & nutritious diet, managing daily stress, and regular exercise is much needed to keep your heart healthy, more so, as your age progresses.




